- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As made)
The Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2009
You are here:
- UK Statutory Instruments
- 2009 No. 1348
- Whole Instrument
- Previous
- Next
More Resources
Status:
This is the original version (as it was originally made).
Statutory Instruments
2009 No. 1348
Health And Safety
The Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2009
Made
27th May 2009
Laid before Parliament
3rd June 2009
Coming into force
1st July 2009
The Secretary of State makes the following Regulations in exercise of the powers conferred by sections 15(1) to (5), (6)(a) and (b) and (8), 43(2) to (6) and 82(3)(a) of, and paragraphs 1, 2(1), 3, 4(1), 6 to 9, 11 to 16 and 20 of Schedule 3 to, the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974(1) as
read with paragraph 1A of Schedule 2 to the European Communities Act 1972(2).
These Regulations make provision for a purpose mentioned in section 2(2) of the European Communities Act 1972 and it appears to the Secretary of State that it is expedient for the reference to the Dangerous Goods Directive to be construed as a reference to that instrument as amended from time to time.
In accordance with section 50(1) and (1AA) of the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974(3) the Secretary of State has consulted the Health and Safety Executive and such other bodies as appear to the Secretary of State to be appropriate.
In accordance with paragraph 2(7) of Schedule 3 to the Railways Act 2005(4) the Secretary of State has consulted the Office of Rail Regulation.
PART 1INTRODUCTORY PROVISIONS
Citation and commencement
1. These Regulations may be cited as the Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2009 and come into force on 1st July 2009.
Interpretation - General
2.—(1) The provisions of this regulation apply for the purposes of interpreting these Regulations.
(2) Any reference in these Regulations to a “Part”, “Chapter”, “Section” or “Sub-section”, unless the context requires otherwise, is to be construed—
(a)in relation to the carriage of goods by road, as a reference to that Part, Chapter, Section or Sub-section of ADR;
(b)in relation to the carriage of goods by rail, as a reference to that Part, Chapter, Section or Sub-section of RID; and
(c)in relation to the carriage of goods by inland waterway, as a reference to that Part, Chapter, Section or Sub-section of ADN.
(3) Where an expression is defined in ADR, RID or ADN and is not defined in these Regulations, it has the same meaning as in—
(a)ADR in relation to carriage by road;
(b)RID in relation to carriage by rail; and
(c)ADN in relation to carriage by inland waterway.
(4) Where an expression is defined in the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive and is not defined in these Regulations, it has the same meaning as in that Directive.
(5) The expressions mentioned in column 1 of the Table have the meanings given in column 2.
Table
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| “the 2007 Regulations” | The Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2007(5). |
| “ADN” | The Regulations annexed to the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Inland Waterway(6), as revised or reissued from time to time. |
| “ADR” | Annexes A and B to the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road(7), as revised or reissued from time to time. But— (a) to the extent that a reference in these Regulations to ADR is a reference to ADR as it applied for the purposes of the 2007 Regulations, it has the same meaning as in the Table in regulation 2 of those Regulations; and (b) in regulation 14(6)(b) it means Annexes A and B as in force on the date in question. |
| “armed forces” | Means— (a) one of Her Majesty’s Forces within the meaning of the Armed Forces Act 2006(8); (b) the Ministry of Defence Police(9); (c) a visiting force within the meaning of Part 1 of the Visiting Forces Act 1952(10); or (d) a headquarters or organisation designated for the purposes of the International Headquarters and Defence Organisations Act 1964(11). |
| “conformity mark” | The mark referred to in article 10(1) of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive, the form of the mark being set out in Annex VII to that Directive. |
| “ COTIF” | The Convention concerning International Carriage by Rail(12), as revised or re-issued from time to time. |
| “the Dangerous Goods Directive” | Directive 2008/68/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24th September 2008 on the inland transport of dangerous goods(13), as amended from time to time. |
| “fire and rescue authority” | The fire and rescue authority under the Fire and Rescue Services Act 2004(14) |
| “the GB competent authority” | The competent authority in Great Britain for the purposes of these Regulations as determined under regulation 25. But a reference to “2007 GB Competent Authority” is a reference to the competent authority in Great Britain for the purposes of the 2007 Regulations. |
| “national carriage” | Carriage that includes carriage in Great Britain and does not include carriage outside the United Kingdom. |
| “relevant authority” | Has the meaning given in section 6 of the Fire (Scotland) Act 2005(15). |
| “RID” | The Annex to the Regulation concerning the international carriage of dangerous goods by rail which forms Appendix C to COTIF(16), as revised or reissued from time to time. But— (a) to the extent that a reference in these Regulations to RID is a reference to RID as it applied for the purposes of the 2007 Regulations, it has the same meaning as in the Table in regulation 2 of those Regulations; and (b) in regulation 14(6)(b) it means the Annex as in force on the date in question. |
| “the security provisions” | The prohibitions and requirements of Chapter 1.10 (including those requirements deemed to be part of ADR in consequence of regulations 7 and 8.) |
| “the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive ” | Council Directive 1999/36/EC of 29th April 1999(17) concerning the approximation of laws of member States relating to common provision for transportable pressure equipment and methods for inspection and for the purposes of these Regulations— (a) a reference in that Directive to Directive 94/55/EC and 96/49/EC is to be treated as a reference to the Dangerous Goods Directive (and the reference to articles 6(1) and 7 of Directive 94/55/EC and articles 6(1) and 7(1) and (2) of Directive 96/49/EC in article 1(4) is to be treated as a reference to article 4 of the Dangerous Goods Directive); and |
| “vehicle” | Has the meaning given in article 2 of the Dangerous Goods Directive except that the words “at least four wheels and” are to be omitted. |
| “wagon” | Has the meaning given in article 2 of the Dangerous Goods Directive. |
Interpretation of ADR, RID and ADN for the purposes of these Regulations
3. For the purposes of these Regulations—
(a)the scope of ADR, RID and ADN is deemed to include national as well as international carriage;
(b)a member State of the Communities which is not a Contracting Party to ADR or ADN is deemed to be a Contracting Party to ADR or ADN (as the case may be);
(c)a member State of the Communities which is not a Member State of COTIF is deemed to be a Member State of COTIF;
(d)a reference in—
(i)ADR or RID to “competent military authority”;
(ii)ADR or ADN to “Contracting Party”; and
(iii)RID to “Member State”,
is to be treated as a reference to “competent authority” unless the context requires otherwise;
(e)Sub-section 1.1.4.4 of RID applies as if the words “or the provisions of the Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2009 in so far as they relate to carriage by road” were included after the words “provisions of ADR”;
(f)Sub-section 1.6.1.12 of ADR is to be treated as reading “The requirements of Section 1.9.5 and Chapter 8.6 do not apply until 31 December 2009.”;
(g)Sub-section 1.6.2.7 is to be treated as reading “Until 30 June 2011 the requirements of 6.2.1.4.1 to 6.2.1.4.4 applicable until 31 December 2008 apply instead of those of 1.8.6, 1.8.7, 6.2.2.9, 6.2.3.6 to 6.2.3.8.”;
(h)Sub-section 1.6.3.35 is to be treated as reading “The requirements of 1.8.6, 1.8.7 and 6.8.4 TA4 and TT9 do not apply before 1 July 2011.”;
(i)Sub-section 1.6.4.34 is to be treated as reading “The requirements of 1.8.6, 1.8.7 and 6.8.4 TA4 and TT9 do not apply before 1 July 2011.”;
(j)the words “The competent authorities of the Contracting Parties may provide that” are omitted from Sub-section 1.8.3.2 of ADR;
(k)the words “The competent authorities of the Member States may provide that” are omitted from Sub-section 1.8.3.2 of RID;
(l)the reference in Sub-section 1.8.3.3 to “national authorities” is to be treated as a reference to “the GB competent authority or an enforcement authority”; and
(m)Sub-section 5.3.4 of RID is omitted.
Application
4.—(1) These Regulations apply in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods by road and by rail.
(2) These Regulations apply in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods by inland waterway but only to the extent that they apply Sub-sections 1.8.3.7 to 1.8.3.16 (which relate to the training and examination system for safety advisers and the connected issuing and renewal of vocational training certificates).
(3) These Regulations do not apply in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods on any part of the Channel Tunnel system.
(4) In this regulation “the Channel Tunnel system” has the meaning given to “the tunnel system” by section 1(7) of the Channel Tunnel Act 1987(18) except that the words “to be” which come before the word “constructed” are omitted.
PART 2PROHIBITIONS AND REQUIREMENTS
Carriage to be in accordance with ADR or RID
5. No person is to carry dangerous goods, or cause or permit dangerous goods to be carried, where that carriage is prohibited by ADR or RID, including where that carriage does not comply with any applicable requirement of ADR or RID.
Alternative placarding requirements to apply to certain national carriage
6.—(1) This regulation applies in relation to national carriage—
(a)in a tank;
(b)in bulk; or
(c)in relation to carriage by rail, by piggyback transport,
where that carriage is by a United Kingdom vehicle or a United Kingdom wagon.
(2) But this regulation does not apply in relation to carriage—
(a)of class 7 goods; or
(b)of any dangerous goods by a vehicle or wagon belonging to or under the responsibility of one of the armed forces.
(3) For the purposes of regulation 5, the requirements of—
(a)Part 1 of Schedule 1 in respect of carriage by road; and
(b)Part 2 of Schedule 1 in respect of carriage by rail,
are deemed to be requirements of Section 5.3.2 and any conflicting requirements in ADR or RID are to be disregarded.
(4) In this regulation—
(a)a “United Kingdom vehicle” means a vehicle registered by the Secretary of State in accordance with section 21(1) of the Vehicle Excise and Registration Act 1994(19) or a trailer being towed by such a vehicle; and
(b)a “United Kingdom wagon” means a wagon used only for carriage within the United Kingdom.
(5) In Schedule 1 “emergency action code” is a reference to the emergency action code for the dangerous goods in question as listed in the Dangerous Goods Emergency Action Code List(20), as revised or reissued from time to time.
Additional security requirements for carriage by road
7.—(1) For the purposes of regulation 5, the requirements set out in paragraphs (2) to (4) are deemed to be requirements of Chapter 1.10 of ADR.
(2) The carrier and the driver of a vehicle which is being used for the carriage of class 1 goods must ensure that—
(a)the carriage is completed within a reasonable length of time having regard to the distance involved;
(b)the class 1 goods are delivered to—
(i)the consignee or the consignee’s agent; or
(ii)a person who is authorised by the consignee to accept custody of the class 1 goods—
(aa)for onward despatch; or
(bb)in circumstances where the consignee has compelling reasons not to accept the goods in accordance with Sub-section 1.4.2.3,
provided they are delivered to qualifying premises;
(c)the goods are unloaded from the vehicle as soon as is reasonably practicable after it arrives at its place of delivery; and
(d)any trailer or container containing class 1 goods is not detached, or removed, from the vehicle unless it is in qualifying premises.
(3) But paragraph (2)(d) does not apply in an emergency.
(4) The carrier of a vehicle used for the carriage of class 1 goods must not remove any class 1 goods from the consignor’s premises unless ready immediately to despatch them to the consignee or a person authorised by the consignee to accept custody in the circumstances referred to in paragraph (2)(b)(ii)(aa).
(5) In this regulation—
(a)“designated parking area” means—
(i)in relation to an airport or railway transhipment depot or siding, an area allocated by the occupier as an area for parking vehicles carrying class 1 goods; and
(ii)in relation to a harbour or harbour area, a parking area designated for the purposes of regulation 32 of the Dangerous Substances in Harbour Areas Regulations 1987(21);
(b)“qualifying premises” means—
(i)premises under the control of the Secretary of State for Defence;
(ii)a safe and secure place; or
(iii)a designated parking area in an airport, a railway transhipment depot or siding or a harbour or harbour area; and
(c)“a safe and secure place” means a place within a site—
(i)in relation to which a person—
(aa)is licensed to manufacture or store explosives under regulation 13 of the Manufacture and Storage of Explosives Regulations 2005(22); or
(bb)is registered in respect of such storage under regulation 11 of those Regulations; or
(ii)in respect of which a certificate of exemption has been granted under the Explosives Act 1875 (Exemption) Regulations 1979(23).
Additional security requirement relating to access
8.—(1) For the purposes of regulation 5, the requirement set out in paragraph (2) is deemed to be a requirement of Chapter 1.10.
(2) A person involved in the carriage of dangerous goods must take all reasonable steps to ensure that unauthorised access to those goods is prevented.
Application of ADR to carriage by private individuals
9.—(1) This regulation applies in relation to the carriage of class 1 goods by road.
(2) For the purposes of regulation 5, the exemption from the prohibitions and requirements of ADR provided for by Sub-section 1.1.3.1(a) of ADR (carriage by private individuals) is to be disregarded.
(3) But paragraph (2) does not apply if the conditions specified in paragraphs (4) and (5) are satisfied.
(4) The net mass of explosive substance being carried does not exceed—
(a)in the case of fireworks, 50 kilograms; and
(b)in the case of other explosives or a combination of fireworks and other explosives, 30 kilograms.
(5) The individual has taken all reasonable steps to ensure that—
(a)the manner in which the class 1 goods are loaded, stowed, carried or unloaded will not create a significant risk or significantly increase any existing risk to the health or safety of any person; and
(b)there is no unauthorised access to the class 1 goods.
Application of ADR to carriage by certain enterprises
10.—(1) This regulation applies in relation to the carriage of class 1 goods by road.
(2) For the purposes of regulation 5, the requirements referred to in paragraph (3) apply to carriage that would, but for this paragraph, be exempt from those requirements because of the exemption set out in Sub-section 1.1.3.1(c) of ADR (carriage by enterprises which is ancillary to their main activity).
(3) The requirements are—
(a)the requirements of ADR in—
(i)Section 7.5;
(ii)Section 8.3.5; and
(iii)special provisions S1:(3) and S1:(6) of Chapter 8.5; and
(b)the requirements deemed to be part of ADR in consequence of regulations 7 and 8.
PART 3EXEMPTIONS
Derogations and transitional provisions
11.—(1) The Secretary of State for Transport may exempt the carriage of dangerous goods from requirements and prohibitions arising under Part 2 of these Regulations.
(2) But paragraph (1) only applies for the purposes of—
(a)implementing a derogation authorised under article 6(2) to (4) of the Dangerous Goods Directive;
(b)maintaining a transitional provision permitted by article 7 of the Dangerous Goods Directive; or
(c)ensuring that carriage to which these Regulations apply, but the Dangerous Goods Directive, ADR or RID does not apply, is carried out in a manner consistent with a derogation or transitional provision referred to at sub-paragraph (a) or (b).
(3) Where any exemption is granted pursuant to paragraph (1), that exemption is to be set out in a document to be called “Dangerous Goods: Approved Derogations and Transitional Provisions”.
(4) The document may be revised in whole or in part from time to time.
(5) In the document the Secretary of State must set out—
(a)the types of carriage to which the exemption applies;
(b)the circumstances in which the exemption applies;
(c)the requirements and prohibitions that do not apply pursuant to paragraph (1); and
(d)any requirements and prohibitions that apply instead.
(6) The Secretary of State may not bring to an end, or substantially alter, an exemption unless those who might be affected have been consulted.
(7) This regulation does not limit the power to issue an authorisation under regulation 12(1).
Authorisations
12.—(1) A person referred to in column 1 of the Table may issue an authorisation to a person or class of persons to carry dangerous goods in circumstances which are contrary to prohibitions and requirements arising under Part 2 of these Regulations providing the conditions specified in column 2 are satisfied in respect of that carriage.
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| The Secretary of State for Transport | The carriage is national carriage |
| The Secretary of State for Defence | The conditions are as follows— (i) the carriage is national carriage; and (ii) either— (aa) the authorisation relates to prohibitions and requirements arising out of functions for which the Secretary of State for Defence is the GB competent authority; or (bb) it is in the interests of national security to disapply the prohibitions and requirements that are the subject of the authorisation; or (b) the carriage is by a vehicle or wagon belonging to or under the responsibility of one of the armed forces and it is not reasonably practicable for operational, training or security reasons related to the role of the armed forces for the prohibitions and requirements disapplied by the authorisation to apply to the carriage. |
| The Health and Safety Executive | The carriage is national carriage and the authorisation relates to prohibitions and requirements arising out of functions for which the Health and Safety Executive is the GB competent authority. |
(2) An authorisation issued pursuant to paragraph (1) must be in writing and must set out—
(a)the carriage that is covered by the authorisation;
(b)the reason that the authorisation is being issued; and
(c)any time limit applicable to the validity of the authorisation.
(3) An authorisation issued pursuant to paragraph (1) may be—
(a)made subject to conditions; and
(b)withdrawn at any time by the provision of a notice in writing to that effect to the person authorised and that notice must set out whether the withdrawal of the authorisation has effect immediately or whether the withdrawal has effect from a specified date.
(4) Any authorisation granted, or deemed to be granted, pursuant to regulation 9(2) or 10(13) of the 2007 Regulations that was in force immediately before the coming into force of these Regulations is deemed to be an authorisation issued pursuant to paragraph (1) of this regulation and subject to the same conditions as were in force immediately before the coming into force of these Regulations.
Reference temperatures and standards
13.—(1) This regulation applies where the GB competent authority has recognised reference temperatures or standards in accordance with regulation 28(1) or (2).
(2) Part 2 does not apply in relation to national carriage to the extent that it imposes requirements on that carriage that conflict with the reference temperatures or standards recognised in accordance with regulation 28(1) or (2).
(3) The exemption set out in paragraph (2) only applies if the tank or pressure receptacle being used for carriage —
(a)is clearly marked or labelled to show that it is suitable for national carriage only; and
(b)does not carry the conformity mark.
Old pressure receptacles
14.—(1) This regulation applies in relation to national carriage.
(2) This regulation applies in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods which is not permitted under Part 2 of these Regulations because the old pressure receptacle used for that carriage cannot, by virtue of its design or construction, satisfy the requirements for the use of pressure receptacles set out in ADR or RID.
(3) Subject to paragraph (5), the requirements in ADR or RID which cannot be complied with are to be disregarded for the purposes of Part 2 of these Regulations if the requirements of paragraph (4) are satisfied.
(4) The requirements are—
(a)the old pressure receptacle has not been subject to modification, major repair or re-rating which has put it outside the scope of the design standard or design specification to which it was originally constructed;
(b)the old pressure receptacle—
(i)has been approved by a person appointed pursuant to regulation 29(2) as being safe for use;
(ii)was found to be safe by an inspection body in accordance with paragraph 5(4) of Schedule 3 to the 2007 Regulations and marked accordingly; or
(iii)was found to be safe by an inspection body or a competent person in accordance with paragraph 4(2) of Schedule 2 to the Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2004(24) and marked accordingly,
and the time elapsed since the approval or the finding that the receptacle was safe does not exceed the intervals for periodic inspection specified in Tables 1 to 3 of Packaging Instruction P200 and Packing Instruction P203 in Section 4.1.4; and
(c)in respect of old pressure receptacles used for the carriage of acetylene, the operator has a written record of—
(i)the tare weight of the old pressure receptacle, including the porous substance and, where relevant, the acetone or other solvent;
(ii)the nature of solvent used; and
(iii)the maximum safe operating pressure of the old pressure receptacle.
(5) An old pressure receptacle which is of seamless construction or has contained acetylene and in relation to which a modification, major repair or re-rating has been undertaken may not be used for the carriage of dangerous goods.
(6) In this regulation “old pressure receptacle” means a cylinder, tube, pressure drum, closed cryogenic receptacle or bundle of cylinders—
(a)constructed—
(i)in the case of cylinders, tubes and cryogenic receptacles, on or before 30th June 2003; and
(ii)in the case of other pressure receptacles, on or before 9th May 2004;
(b)which did not meet the design and construction requirements applicable to that receptacle that were set out in ADR or RID as in force on the date construction was completed;
(c)which did comply with the design and construction requirements imposed under the law of the United Kingdom in force on the date construction was completed; and
(d)which has not been subject to a reassessment of conformity pursuant to a provision of the law of United Kingdom or another EEA State giving effect to article 5 of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive (including regulation 21 of these Regulations).
Carriage within the perimeter of an enclosed area
15. Part 2 of these Regulations does not apply in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods where such carriage is wholly performed within the perimeter of an enclosed area.
Carriage by road other than by vehicles
16.—(1) This regulation applies in relation to carriage by road.
(2) Part 2 of these Regulations does not apply in relation to carriage where that carriage is not undertaken by a vehicle.
Instruments of war and related material
17. Part 2 of these Regulations does not apply in relation to the carriage of class 7 goods by a vehicle or wagon belonging to, or under the responsibility of, one of the armed forces where those goods—
(a)are, or form part of, an instrument of war;
(b)are required for research into, or the development or production of, any such instrument or part of such instrument; or
(c)are produced in the course of, or in connection with, such research, development or production.
Nuclear material
18.—(1) Part 2 does not apply in relation to the carriage of Category I/II nuclear material or Category III nuclear material to the extent that it requires compliance with the security provisions.
(2) In this regulation—
(a)“Category I/II nuclear material” has the meaning given in regulation 3(3) of the Nuclear Industries Security Regulations 2003(25); and
(b)“Category III nuclear material” has the meaning given in regulation 3(4) of the Nuclear Industries Security Regulations 2003.
PART 4TRANSPORTABLE PRESSURE EQUIPMENT
Conformity assessment
19.—(1) This regulation applies to transportable pressure equipment within the scope of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive by virtue of article 1(2)(a) of that Directive.
(2) Subject to regulation 20, equipment may only be placed on the market or put into service if the four obligations set out in this regulation are all satisfied.
(3) The first obligation is that the equipment meets the requirements of—
(a)the Dangerous Goods Directive; or
(b)if applicable, article 3(4) of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive.
(4) The second obligation is that the fact that the equipment satisfies the first obligation is demonstrated by the conformity assessment procedures mentioned in article 3(1) and (2) of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive.
(5) The third obligation is that those conformity assessment procedures are carried out by a notified body.
(6) The fourth obligation is that the marking requirements set out in article 10 of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive that are applicable to conformity assessment are complied with in relation to that equipment.
(7) For the purposes of these Regulations, a reference in Part I of Annex IV to the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive to “national authorities” is to be treated as if it were a reference to “competent authority”.
Conformity assessment – national carriage
20.—(1) Transportable pressure equipment to which regulation 19 applies may be—
(a)placed on the market; or
(b)put into service,
for use in national carriage if the three obligations set out in this regulation are all satisfied.
(2) The first obligation is that the equipment satisfies the conformity assessment referred to in article 4(4) of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive.
(3) The second obligation is that the assessment is carried out by an approved body.
(4) The third obligation is that the marking requirements set out in article 10 of the Directive as read with article 4(2) that are applicable to conformity assessment are complied with.
Reassessment of conformity
21.—(1) This regulation applies to transportable pressure equipment within the scope of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive by virtue of article 1(2)(b) of that Directive.
(2) Equipment may be reassessed for conformity in accordance with this regulation.
(3) The equipment is to be—
(a)reassessed by a notified body in accordance with the procedure set out in Part II of Annex IV to the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive; and
(b)marked in accordance with the requirements of article 10 of that Directive that are applicable to the reassessment of conformity.
(4) But if the equipment has been manufactured in series to a design type which has been reassessed by a notified body in accordance with paragraph (3)(a), the procedure set out in Part II of Annex IV may be undertaken by an approved body and references in that Part to “notified body” are to treated as references to “approved body”.
Periodic inspection and repeated use
22.—(1) This regulation applies to transportable pressure equipment within the scope of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive by virtue of article 1(2)(c) of that Directive.
(2) If the equipment bears a marking referred to in article 10(1) or (2) of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive or the marking for gas cylinders referred to in the second indent of article 1(2)(c) of that Directive, it is to be subject to periodic inspection in accordance with the requirements of article 6(1) of the Directive.
(3) Periodic inspections of tanks are permitted in the manner described in the second paragraph of article 6(1).
(4) The marking requirements applicable to periodic inspections set out in article 10 of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive are to be complied with in relation to the equipment.
Misleading and other markings
23.—(1) No person is to affix a marking on transportable pressure equipment which is likely to mislead third parties with regard to the meaning or the graphics of the conformity mark.
(2) Any other marking may be affixed to transportable pressure equipment provided that the visibility and legibility of the conformity mark is not reduced.
PART 5RADIOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES
Radiological emergencies
24.—(1) This regulation applies in relation to the carriage of class 7 goods.
(2) The requirements of Schedule 2 are to be complied with in relation to radiological emergencies.
(3) But paragraph (2) does not apply in relation to carriage by vehicles or wagons belonging to or under the responsibility of one of the armed forces.
(4) For the purposes of these Regulations—
(a)“radiological emergency” means a situation arising during the course of the carriage of a consignment that requires urgent action in order to protect workers, members of the public or the population (either partially or as a whole) from exposure;
(b)“exposure” means being exposed to ionising radiation; and
(c)“ionising radiation” means the transfer of energy in the form of particles or electromagnetic waves of a wavelength of 100 nanometres or less, or a frequency of 3x1015 hertz or more, capable of producing ions directly or indirectly.
PART 6GB COMPETENT AUTHORITY FUNCTIONS
Competent authority
25.—(1) The competent authority in Great Britain for the purposes of these Regulations is determined in accordance with paragraphs (2) to (5).
(2) Subject to paragraph (3), the Health and Safety Executive is the competent authority for class 1 goods in relation to—
(a)classification pursuant to Section 2.2.1;
(b)special provisions 16, 178, 266, 271, 272, 278, 288, 309, 311 and 645 of Chapter 3.3;
(c)mixed packing instruction MP21 of Section 4.1.10, Sub-sections 4.1.5.15 and 4.1.5.18;
(d)the design approval of containers or compartments, in accordance with note a to Sub-section 7.5.2.2; and
(e)the functions in respect of mobile explosives manufacturing units mentioned in Sub-sections 6.12.5 and 7.5.5.2.3.
(3) The competent authority is the Secretary of State for Defence for functions—
(a)in relation to military explosives for—
(i)classification pursuant to Section 2.2.1;
(ii)special provisions 16, 178, 266, 271 and 645 of Chapter 3.3;
(iii)mixed packing instruction MP21 of Section 4.1.10, Sub-sections 4.1.5.15 and 4.1.5.18;
(iv)special provision W2 of Section 7.2.4; and
(v)the design approval of containers or compartments, in accordance with note a to Sub-section 7.5.2.2; and
(b)in relation to class 7 goods which—
(i)are, or form part of, an instrument of war;
(ii)are required for research into, or the development or production of, any such instrument or part of such instrument; or
(iii)are produced in the course of, or in connection with, such research, development or production.
(4) The competent authority for the functions set out in Sub-sections 1.9.5.1, 1.9.5.3.1 and 1.9.5.3.8 of ADR is the traffic authority responsible for the road that passes through the tunnel.
(5) The Secretary of State for Transport is the competent authority for all other functions.
(6) The GB competent authority may appoint a person to carry out a function of the GB competent authority under these Regulations and a reference in these Regulations to the performance of the function by the GB competent authority is to be treated as including a reference to the performance of the function by the person appointed.
(7) The person may be appointed to carry out the function in particular circumstances or generally.
(8) Paragraphs (9) and (10) apply if the 2007 GB competent authority appointed, or was deemed by regulation 67(5) of the 2007 Regulations to have appointed, a person to perform a competent authority function pursuant to regulation 67(1) of those Regulations and that appointment had effect immediately before the coming into force of these Regulations.
(9) The person appointed, or deemed appointed, under the 2007 Regulations is deemed to be a person appointed pursuant to paragraph (6) to perform the equivalent function in ADR or RID.
(10) But in the case of a function performed in relation to carriage by inland waterway, the GB competent authority is to be deemed to have performed the function under the equivalent provision of ADN as it was performed, or deemed performed, under ADR pursuant to regulation 67(1) of the 2007 Regulations.
(11) In this regulation—
(a)“military explosives” has the same meaning as in regulation 2(1) of the Classification and Labelling of Explosives Regulations 1983(26); and
(b)“traffic authority” is to be construed in accordance with section 121A of the Road Traffic Regulation Act 1984(27).
Functions of the GB competent authority arising under ADR, RID and ADN
26. The GB competent authority is to perform those functions that are identified in ADR, RID and ADN as being the functions of a competent authority.
Fees in relation to functions of the GB competent authority
27.—(1) This regulation applies where a person has asked the GB competent authority to perform a function which is, by virtue of regulation 26, a function of the GB competent authority.
(2) A fee may be charged for, or in connection with, the performance of the function by, or on behalf of, the GB competent authority.
(3) Any fee charged must be reasonable for the work performed or to be performed.
(4) But in relation to a function mentioned in regulation 29(3), paragraph 1(2) and (3) of Schedule 3 applies instead of paragraphs (2) and (3) of this regulation.
GB competent authority functions relating to reference temperatures and standards
28.—(1) The GB competent authority may recognise different reference temperatures from those set out in—
(a)paragraphs (5)(b) and (c) of packing instruction P200 of Section 4.1.4; or
(b)Sub-sections 4.2.2.7.2, 4.3.3.2.2 or 4.3.3.2.3,
in relation to the filling of pressure receptacles and tanks intended to be used only for the national carriage of liquefied gas.
(2) The GB competent authority may recognise standards for the construction of the shell of a tank intended to be used only for the national carriage of liquefied gas which specify—
(a)a different design reference temperature for the shell of the tank from that set out in Sub-section 6.7.3.2.1; or
(b)a different test pressure for the shell of the tank from that set out in Sub-sections 4.3.3.2.2 and 4.3.3.2.3,
provided that the temperature or pressure specified in the standard is such that it will ensure that the shell is safe and suitable for its intended use.
Appointments by the GB competent authority
29.—(1) Paragraph (2) applies in respect of equipment which under these Regulations may not be used in connection with the carriage of dangerous goods unless it has been approved for that use.
(2) The GB competent authority may appoint such persons as it thinks fit to determine whether the equipment should be approved and, if so, to approve that equipment for use.
(3) Where it is a function of the GB competent authority, by virtue of regulation 26, to approve or authorise a body or expert to carry out, witness, supervise or decide to waive an inspection, examination, test or approval in respect of equipment used in connection with the carriage of dangerous goods, that function is to be performed by the appointment of a person pursuant to paragraph (2).
(4) In respect of the appointment of a person to carry out the functions of a notified body for the purposes of Part 4 of these Regulations, the GB competent authority may not appoint a person pursuant to paragraph (2) unless that person satisfies the criteria set out in Annexes I and II to the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive.
(5) In respect of the appointment of a person to carry out the functions of an approved body for the purposes of Part 4 of these Regulations, the GB competent authority may not appoint a person pursuant to paragraph (2) unless that person satisfies the criteria set out in Annexes I and III to the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive.
(6) Schedule 3 has effect in relation to the making of appointments pursuant to paragraph (2).
Certain functions to be deemed to have been performed by the GB competent authority
30.—(1) Paragraphs (3) and (4) apply if—
(a)the 2007 GB competent authority performed, or was deemed by regulation 70 of the 2007 Regulations to have performed, a function pursuant to regulation 66(1) of those Regulations; and
(b)the action taken by the 2007 GB competent authority, as a consequence of the performance of the function, had effect immediately before the coming into force of these Regulations.
(2) But paragraphs (3) and (4) do not apply where the function was performed, or deemed performed, by appointment in accordance with regulation 69(2) of the 2007 Regulations.
(3) The GB competent authority is deemed to have performed the function pursuant to regulation 26 under the same provision of ADR or RID as it was performed, or deemed performed, pursuant to regulation 66(1).
(4) In the case of a function performed in relation to carriage by inland waterway, the GB competent authority is to be deemed to have performed the function under the equivalent provision of ADN as it was performed, or deemed performed, under ADR pursuant to regulation 66(1).
PART 7MISCELLANEOUS
Keeping and provision of information
31.—(1) An accident report of the kind referred to in Sub-section 1.8.3.6 is to be provided to the GB competent authority or enforcement authority if requested.
(2) A written record of the information contained in the transport document described in Chapters 5.4 and 5.5 is to be kept for a period of three months after the completion of the carriage in question.
Enforcement
32.—(1) The enforcing authorities for these Regulations are—
(a)the Health and Safety Executive in relation to road and rail;
(b)the Secretary of State for Transport in relation to road and inland waterways; and
(c)the chief officer of police of each area in relation to road.
(2) But the Health and Safety Executive is not the enforcing authority in relation to rail to the extent that the Office of Rail Regulation is the enforcing authority pursuant to regulation 3(1) of the Health and Safety (Enforcing Authority for Railways and Other Guided Transport Systems) Regulations 2006(28).
(3) Paragraphs (1) and (2) are subject to paragraph (4).
(4) The Secretary of State for Transport is the only enforcing authority to the extent that these Regulations require compliance with the security provisions.
Revocation
33. The 2007 Regulations are revoked.
Signed by the authority of the Secretary of State
Paul Clark
Parliamentary Under Secretary of State
Department for Transport
27th May 2009
Regulation 6(3)
SCHEDULE 1PLACARDS, MARKS AND PLATE MARKINGS FOR NATIONAL CARRIAGE
PART 1CARRIAGE OF GOODS BY ROAD
Hazard Identification Numbers to be replaced by Emergency Action Codes (road)
1. When displaying the orange-coloured plates provided for by Sub-sections 5.3.2.1.2 and 5.3.2.1.4, the emergency action code for the substance in question must be displayed instead of the hazard identification number.
Display of the orange-coloured plate if one type of dangerous good is being carried (road)
2. If one type of dangerous good is being carried —
(a)the orange-coloured plates referred to in paragraph 1 must be displayed in accordance with the provisions of Sub-sections 5.3.2.1.2 and 5.3.2.1.4 which are applicable to the goods, battery-vehicle, tank-vehicle, transport unit or container in question; and
(b)an identical orange-coloured plate must be affixed to the rear of the transport unit in place of the orange-coloured plate to be affixed to the rear of the transport unit pursuant to Sub-section 5.3.2.1.1.
Display of the orange-coloured plate if more that one type of dangerous good is being carried (road)
3.—(1) If more than one type of dangerous good is being carried in a tank or in bulk in a transport-unit or a battery-vehicle or a tank-vehicle with more than one tank, element or container—
(a)the orange-coloured plates referred to in paragraph 1, must be displayed in accordance with the provisions of Sub-sections 5.3.2.1.2 and 5.3.2.1.4 which are applicable to the goods, transport unit, battery-vehicle, tank-vehicle or container in question except that—
(i)only one on each side of the transport unit, tank, tank compartment, element of a battery-vehicle, or container in question, parallel to the longitudinal axis, is to bear the emergency action code; and
(ii)the remaining plates must bear only the UN number and must be 150mm in height; and
(b)an orange-coloured plate must be affixed to the rear of the battery-vehicle, tank-vehicle or transport unit in question which must be identical to the plates referred to in Paragraph (a), except that it is to display the emergency action code only in the top half of the plate.
(2) But if more than one type of dangerous good is being carried in a transport unit or a tank-vehicle with more than one tank and those goods are—
(a)UN 1202 DIESEL FUEL or GAS OIL or HEATING OIL, LIGHT;
(b)UN 1203 PETROL or MOTOR SPIRIT or GASOLINE; or
(c)UN 1223 KEROSENE,
then the requirements of paragraph 2 must be met, except that the orange-coloured plates need only bear the emergency action code and UN number for the most hazardous of the dangerous goods being carried.
Telephone number to be used to obtain specialist advice to be displayed (road)
4.—(1) If dangerous goods are being carried in tanks a telephone number where specialist advice concerning the dangerous goods in question can be obtained in English at any time during carriage must be displayed—
(a)at the rear of the transport unit;
(b)on both sides of—
(i)any tank;
(ii)the frame of any tank; or
(iii)the transport unit; and
(c)in the immediate vicinity of the orange-coloured plates displaying the emergency action codes,
and must be in black digits of not less than 30mm in height against an orange-coloured background.
(2) The phrase “consult local depot” or “contact local depot” may be substituted for the telephone number if—
(a)the name of the carrier is clearly identifiable from the marking on any tank or the transport unit;
(b)as regards England and Wales, the fire and rescue authority or, as regards Scotland, the chief officer of the relevant authority of each area through which the transport unit will carry the dangerous goods has been notified in writing of the address and telephone number of the relevant local depot; and
(c)each fire and rescue authority or chief officer, as referred to in Paragraph (b), has indicated, in writing, satisfaction with the arrangements.
Use of hazard warning panels (road)
5.—(1) The information required to be displayed on placards and orange-coloured plates pursuant to Section 5.3.1 and paragraphs 1 to 3 and the information required to be displayed pursuant to paragraph 4 may all be shown on hazard warning panels provided that any such panel meets the conditions set out in sub-paragraph (2) and, if relevant, sub-paragraph (3).
(2) The conditions referred to in sub-paragraph (1) for a hazard warning panel are that—
(a)it must be displayed in accordance with paragraphs 1 to 4 as if it were an orange-coloured plate;
(b)it must be orange-coloured, except the part incorporating the placard which must be white;
(c)the placard must be not less than 200mm by 200mm, with a line of the same colour as the relevant symbol not more than 12.5mm inside the edge and running parallel to it;
(d)if more than one placard is to be incorporated in the panel, those placards must be adjacent in the same horizontal plane;
(e)it must conform to the figure in sub-paragraph (4); and
(f)it must be clearly visible.
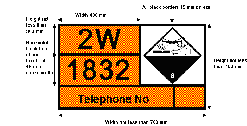
(3) If dangerous goods are carried in a tank which was constructed on or after 1st January 2005, the orange-coloured plate must be indelible and remain legible after it has been engulfed in fire for 15 minutes.
(4) The figure is—
PART 2CARRIAGE OF GOODS BY RAIL
Hazard Identification Numbers to be replaced by Emergency Action Codes (rail)
6. When displaying the orange-coloured plates provided for by Section 5.3.2, the emergency action code for the substance in question must be displayed instead of the hazard identification number.
Telephone number to be used to obtain specialist advice to be displayed (rail)
7. If dangerous goods are being carried in tanks, a telephone number where specialist advice concerning the dangerous goods in question may be obtained in English at any time during carriage must be displayed—
(a)in the immediate vicinity of each orange-coloured plate; and
(b)against an orange-coloured background in black digits of not less than 30mm in height.
Use of hazard warning panels (rail)
8.—(1) The information required to be displayed on placards and orange-coloured plates in accordance with Section 5.3.1 and paragraph 6 and the telephone number required to be displayed pursuant to paragraph 7 may all be shown on hazard warning panels provided that the panel meets the conditions set out in sub-paragraph (2).
(2) The conditions referred to in sub-paragraph (1) for a hazard warning panel are that it must—
(a)be displayed in accordance with paragraph 7 as if it were an orange-coloured plate; and
(b)comply with the requirements of paragraphs 5(2)(b) to (f).
Regulation 24(2)
SCHEDULE 2RADIOLOGICAL EMERGENCIES
Interpretation
1. In this Schedule, the expressions mentioned in column 1 of the Table have the meanings given in column 2—
Table
| Column 1 | Column 2 |
|---|---|
| “assist in the intervention” | The taking of such steps, as it is reasonable and practicable in the prevailing circumstances to take, in order to prevent or decrease exposure. The circumstances to be taken into account include— (a) the weather conditions; (b) the time of the occurrence of the emergency; (c) the distribution of the local population; (d) the nature and content of the package involved; (e) the stability of the class 7 goods involved; (f) the nature of the local geography and ecology; (g) any other prevailing hazards; and (h) the relative importance of the emergency in relation to other calls that are being made upon the emergency services. |
| “intervention” | A human activity that prevents or decreases the exposure of persons to radiation from a radiation emergency or from an event which could lead to a radiation emergency, by acting on the sources of radiation, the paths by which such radiation may be transmitted to persons and on persons themselves. |
Information to the public about health protection measures
2.—(1) Every consignor, carrier and consignee carrying out the transport of a consignment must—
(a)ensure that any members of the public who are in an area in which, in the opinion of the GB competent authority, they are likely to be affected by a radiological emergency arising from the undertaking of that carrier, consignor or consignee are supplied, in the appropriate manner approved by the GB competent authority and without their having to request it, with at least the information set out in sub-paragraph (2); and
(b)make that information publicly available, which includes endeavouring to enter into an agreement or arrangement with the local authority in the area referred to in Paragraph (a) for the dissemination by that authority of the information required to be supplied to members of the public in accordance with that Paragraph.
(2) The following is the information that is to be supplied and made available—
(a)the basic facts about the radioactivity and its effects on persons and on the environment;
(b)the various types of radiological emergency possible and their consequences for the general public and the environment;
(c)the emergency measures envisaged to alert, protect and assist the general public in the event of the occurrence of a radiological emergency;
(d)appropriate information on action to be taken by the general public in the event of the occurrence of a radiological emergency; and
(e)the appropriate local authority responsible for implementing the emergency measures and action referred to in Paragraphs (c) and (d).
(3) In preparing the information to be supplied and made available, the carrier, consignor or consignee must—
(a)consult the GB competent authority, but remain responsible for the accuracy, completeness and form of the information supplied; and
(b)endeavour to enter into an agreement or arrangement with the local authority in whose area the carrier, consignor or consignee is situated with respect to the dissemination by that authority of the information to members of the public.
(4) The information supplied and made available must be updated—
(a)at regular intervals;
(b)whenever significant changes to any of the matters mentioned in sub-paragraph (2) take place; and
(c)in any event, at least every 3 years.
(5) When information is updated in accordance with sub-paragraph (4) it must again be supplied and made publicly available in accordance with sub-paragraph (2).
Duties with respect to the monitoring of particular persons
3.—(1) Any—
(a)employee or agent of a consignor, carrier or consignee; or
(b)person of whose services a consignor, carrier or consignee makes use in the carriage of dangerous goods,
who assists in an intervention and is liable to be subjected to emergency exposure must be treated as being a person classified pursuant to regulation 20 of the Ionising Radiations Regulations 1999(29) (“the 1999 Regulations”) and, accordingly, the consignor, carrier or consignee (as the case may be) has the same duties with regard to the monitoring of such persons as are imposed upon an ‘employer’ by regulations 21 to 26 of the 1999 Regulations.
(2) To the extent that it is necessary in order to save human lives, an emergency exposure is permitted as a result of which the dose limit specified in paragraph 1, 2, 6, 7 or 8 of Schedule 4 (Dose Limits) to the 1999 Regulations will be exceeded, provided that the person who is proposed to be subjected to a dose in excess of the limit provided for in the relevant paragraph is a volunteer and has been informed of the risks involved in the intervention.
(3) In this paragraph, “emergency exposure” means an exposure of a person engaged in an activity of, or associated with, the response to a radiation emergency or potential emergency in order to bring help to endangered persons, prevent exposure of a large number of persons or save a valuable installation or goods where one of the individual dose limits referred to in paragraphs 1 or 2 of Part 1 of Schedule 4 to the 1999 Regulations could be exceeded.
Duties of consignor and carrier with regard to the preparation of emergency arrangements
4.—(1) Before the carriage of a package begins, the consignor of that package must ensure that there is a plan in writing setting out such emergency arrangements as are appropriate for the carriage of that package.
(2) The plan must be prepared having regard to—
(a)the principle that intervention is to be undertaken only if the damage due to the radiation resulting from the radiation emergency is sufficient to justify the potential harm and the potential cost (including the social cost) of that intervention;
(b)the principle that the form, scale and duration of the intervention should ensure that the benefit to health will be greater than any harm that might be associated with the intervention itself;
(c)the dose limits provided for in Schedule 4 to the Ionising Radiations Regulations 1999; and
(d)the levels of radiation dose applicable in an emergency that are specified by the Health Protection Agency pursuant to its functions under section 3 of the Health Protection Agency Act 2004(30).
(3) To the extent that the plan is used in relation to carriage on more than one occasion, the consignor must review and, whenever necessary, revise the emergency arrangements and must ensure that at suitable intervals they are tested.
Duties of drivers, carriers and consignors in the event of the occurrence of a radiological emergency
5.—(1) The driver of a vehicle or train carrying class 7 goods who discovers, or has reason to believe, that a notifiable event has occurred in relation to the transport unit or train must—
(a)immediately notify—
(i)the police;
(ii)(where appropriate), as respects England and Wales, the fire and rescue authority and, as respects Scotland, the chief officer of the relevant authority; and
(iii)the consignor,
of that event;
(b)initiate the emergency arrangements in respect of any radiological emergency; and
(c)assist in the intervention that is made in connection with that radiological emergency.
(2) The carrier of class 7 goods who becomes aware of the occurrence of a notifiable event in relation to those goods must—
(a)immediately notify—
(i)the police (unless the driver of the transport unit or train has already done so); and
(ii)the GB competent authority,
of that event;
(b)assist in the intervention that is made in connection with any radiological emergency; and
(c)as soon as is reasonably practicable, arrange for the examination of the load so as to determine whether contamination has arisen and, if it has, to arrange for the safe disposal of any part of the load that has been contaminated and for the decontamination of the transport unit or train.
(3) If a consignor of class 7 goods becomes aware of the occurrence of a notifiable event in relation to those goods, the consignor must—
(a)immediately notify—
(i)the police; and
(ii)the GB competent authority,
of that event (unless either the driver or the carrier has already done so);
(b)assist in the intervention that is made in connection with any radiological emergency; and
(c)provide the GB competent authority with details of the incident that gave rise to that emergency.
(4) If a consignor of class 7 goods becomes aware that emergency arrangements have been initiated in relation to those goods, the consignor must notify the GB competent authority of the initiation of those arrangements even if, in the event, no intervention was made pursuant to those arrangements.
(5) If a notifiable event occurs the carrier must ensure that a report is made forthwith to the GB competent authority.
(6) The report required under sub-paragraph (5) must be in a form which has been approved by the GB competent authority and must contain all relevant information which the GB competent authority has communicated to the carrier that it considers necessary.
(7) In this paragraph—
(a)“notifiable event” means—
(i)a radiological emergency,
(ii)the theft or loss of the class 7 goods being carried; or
(iii)an occurrence subject to report as construed in accordance with Sub-section 1.8.5.3; and
(b)“initiate the emergency arrangements” means the taking of such steps as it is reasonable and practicable to take in order to put into effect the actions that have been planned for in the emergency arrangements.
Packages involved in a radiological emergency
6. A package that has been involved in a radiological emergency must not be carried or caused to be carried unless the consignor or the consignor’s agent has examined it and the consignor is satisfied that it complies with the requirements of these Regulations and has issued a certificate to that effect.
Power of the competent authority to require documents and require testing, rehearsal and revision of the emergency arrangements
7.—(1) The consignor and carrier must provide to the GB competent authority, within such reasonable period as the GB competent authority may specify, such documents relating to the emergency arrangements as may have been requested by the GB competent authority.
(2) To the extent required by a notice in writing served on the consignor or carrier by the GB competent authority, the consignor or carrier must test, rehearse and revise the emergency arrangements.
Regulation 29(6)
SCHEDULE 3APPOINTMENTS
Applications for appointment
1.—(1) An application for appointment must be made in a manner approved by the GB competent authority.
(2) A fee may be charged for, or in connection with, the consideration by, or on behalf of, the GB competent authority of an application for appointment.
(3) Any fee charged must be reasonable for the work performed or to be performed.
Appointment by the GB competent authority
2.—(1) The GB competent authority must make any appointment in writing.
(2) An appointment may be made subject to such conditions as the GB competent authority considers appropriate and, in particular, those conditions may—
(a)restrict the scope of the appointment to equipment of a particular description;
(b)require markings of a particular description to be affixed to equipment by or on behalf of the appointee in connection with the giving, or the refusal to give, approval; and
(c)apply upon or following termination of the appointment.
(3) An appointment may be for the time being or for such period as may be specified in the appointment.
(4) If for any reason an appointment is terminated, the GB competent authority may—
(a)give such directions—
(i)to the person whose appointment has been terminated; or
(ii)to another person who has been appointed, or deemed appointed, pursuant to these Regulations,
for the purpose of making such arrangements for the determination of outstanding applications for approval of equipment as it considers appropriate and the person to whom the directions are given must comply with them; and
(b)authorise another person to take over the functions of the appointee whose appointment has been terminated in respect of such cases as it may specify.
Fees that may be charged by appointees
3.—(1) An appointee may charge a fee for, or in connection with, the carrying out of a function for which the appointment has been made.
(2) The fee must not exceed—
(a)the costs incurred or to be incurred by the appointee in performing the function; and
(b)an amount on account of profit which is reasonable in the circumstances having regard to—
(i)the character and extent of the work done or to be done by the appointee; and
(ii)the commercial rate normally charged on account of profit for that work or similar work.
The inspection of appointees
4.—(1) An appointee is to be subject to such inspection by, or on behalf of, the GB competent authority as is necessary to ensure compliance with any condition specified in the appointment.
(2) The inspection referred to in sub-paragraph (1) may include the examination of premises, equipment and documents and the appointee must provide such copies, facilities, assistance and information as are reasonably required for the purpose of the inspection.
(3) A fee which is reasonable for the work performed, or to be performed, is to be payable by the appointee in respect of any inspection undertaken by, or on behalf of, the GB competent authority in accordance with sub-paragraph (1).
EXPLANATORY NOTE
(This note is not part of the Regulations)
These Regulations impose requirements and prohibitions in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods by road and by rail and, in so far as they relate to safety advisers, by inland waterway. In doing so they implement certain Directives as respects Great Britain.
First, the Regulations implement Directive 2008/68/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24th September 2008 on the inland transport of dangerous goods (O.J. L260, 30.9.2008, p. 13). This Directive applies the Annexes to the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Road signed at Geneva on 30th September 1957, as amended (“ADR”) (Current Edition: 2009), the Annex to the Regulation concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Rail (“RID”) which forms Appendix C to the Convention concerning International Carriage by Rail (“ COTIF”) (Current Edition: 2009) and the Regulations annexed to the European Agreement concerning the International Carriage of Dangerous Goods by Inland Waterway (“ADN”) (Current edition: 2009). These Regulations only apply the provisions of ADN in respect of safety adviser qualifications.
Secondly, the Regulations implement Council Directive 1999/36/EC of 29th April 1999 on transportable pressure equipment (O.J. No. L138, 1.6.1999, p. 20) as last amended by Commission Directive 2002/50/EC of 6 June 2002 (O.J. No. L149, 7.6.2002, p. 28).
Thirdly, the Regulations implement Article 5 of Title II (Prior Information) of Council Directive 89/618/Euratom of 27th November 1989 on informing the general public about health protection measures to be applied and steps to be taken in the event of a radiological emergency (O.J. No. L357, 7.12.1989, p. 31) and Title IX, Section 1 (Intervention in cases of radiological emergency) of Council Directive 96/29/Euratom of 13th May 1996 laying down basic safety standards for the protection of the health of workers and the general public against the dangers arising from ionizing radiation (O.J. No. L159, 29.6.1996, p. 1), in so far as Section 1 of Title IX is relevant to carriage by road and by rail.
The implementation of 1999/36/EC, 89/618/Euratom and 96/29/Euratom replaces the implementation of the same Directives (or parts of Directives) made by the Carriage of Dangerous Goods and Use of Transportable Pressure Equipment Regulations 2007 (the 2007 Regulations) (S.I. 2007/1573).
Part 1 of the Regulations contains introductory provisions. Regulations 2 and 3 contain interpretation provisions. Regulation 4 sets out the manner in which the Regulations apply.
Part 2 of the Regulations provides for prohibitions and requirements to apply in relation to the carriage of dangerous goods. Regulation 5 prohibits carriage other than in accordance with ADR and RID. Regulation 6 imposes, by reference to Schedule 1, different placarding requirements to those in ADR and RID in respect of national carriage by certain vehicles. Regulation 7 deems certain security requirements relating to class 1 goods to be requirements of ADR for the purposes of regulation 5. Regulation 8 deems a requirement relating to access to goods to be a requirement of ADR and RID for the purposes of regulation 5. Regulation 9 imposes the prohibitions and requirements of ADR on carriage by private individuals for the purposes of regulation 5 unless certain conditions are met. Regulation 10 imposes certain requirements of ADR (including deemed requirements) on carriage by certain enterprises for the purposes of regulation 5.
Part 3 of the Regulations provides for exemptions from Part 2. Regulation 11 allows the Secretary of State for Transport to exempt carriage where such an exemption is permitted as a derogation or a transitional provision under the Dangerous Goods Directive or where the exemption provides for carriage consistent with a derogation or transitional provision. Regulation 12 provides that, in certain circumstances, the Secretary of State for Transport, the Secretary of State for Defence and the Health and Safety Executive may issue authorisations permitting carriage which would otherwise contravene Part 2 of the Regulations. Other regulations provide for exemptions relating to reference temperatures and standards (regulation 13), old pressure receptacles (regulation 14), enclosed areas (regulation 15), carriage other than by vehicles (regulation 16), instruments of war (regulation 17) and nuclear material (regulation 18).
Part 4 of the Regulations applies the provisions of the Transportable Pressure Equipment Directive for placing transportable pressure equipment on the market (regulations 19 and 20), reassessing the conformity of existing transportable pressure equipment (regulation 21), inspections (regulation 22) and the restriction on the use of misleading markings (regulation 23).
Part 5 of the Regulations (regulation 24), by the introduction of Schedule 2, implements the requirements of Article 5 of Title II of 89/618/Euratom and Section 1 of Title IX of 96/29/Euratom in relation to carriage by road and by rail.
Part 6 of the Regulations sets out provisions and obligations in relation to competent authority functions. Regulation 25 determines who the competent authority in Great Britain is. Regulation 26 provides that the competent authority in Great Britain is to perform the functions of a competent authority set out in ADR, RID and ADN (as applied by the Regulations). Regulation 27 provides that fees may be charged in connection with the performance of competent authority functions arising under regulation 26. Regulation 28 provides for a competent authority function in respect of reference temperatures and standards. Regulation 29 allows for the appointment of people to approve equipment used in connection with the carriage of dangerous goods. Regulation 30 deems certain functions done under the 2007 Regulations to be done under these Regulations.
Part 7 of the Regulations contains miscellaneous provisions concerning the keeping and provision of information (regulation 31), enforcement (regulation 32) and the revocation of the 2007 Regulations (regulation 33).
ADR and ADN (both the agreements and the Annexes) may be downloaded without charge from the relevant parts of the United Nations Economic Commission for Europe website which is:
for ADR: http://www.unece.org/trans/danger/publi/adr/adr_e.html
for ADN: http://www.unece.org/trans/danger/adn-agree.html
COTIF (including the protocol of Vilnius and Appendix C to COTIF (but not the text of the Annex to the Appendix)) may be downloaded without charge from the relevant part of the Intergovernmental Organisation for International Carriage by Rail (known as OTIF) website which is:
Print copies of the 2009 editions of ADR, RID (including the text of the Annex to Appendix C) and ADN are available for purchase, including from the Stationery Office:
http://www.tsoshop.co.uk/bookstore.asp
The European Directives referred to in these Regulations may be downloaded without charge from the European Union Law Website (EURLEX):
http://eur-lex.europa.eu/en/index.htm
A document issued by the Secretary of State for Transport pursuant to regulation 11(3) of these Regulations will be published by the Stationery Office. It will also be available to be downloaded from the Department for Transport website which is:
An impact assessment of the effect that this instrument will have on the costs of business and the voluntary sector and a Transposition Note may be obtained from the Dangerous Goods Division of the Department for Transport, Zone 2/24, Great Minster House, 76 Marsham Street, London, SW1P 4DR. The telephone number is 020 7944 5706 and the e-mail address is dangerousgoods@dft.gsi.gov.uk. Both documents may also be downloaded from the Department for Transport website and are annexed to the Explanatory Memorandum which is available alongside the instrument on the OPSI website (www.opsi.gov.uk).
1974 c.37; section 1(1)(c) was modified by the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act (Application to Environmentally Hazardous Substances) Regulations 2002 (S.I. 2002/282) to which relevant amendments have been made by S.I. 2004/463, 2005/1308, 2007/1332 and 2009/318. Section 15(1) was amended by the Employment Protection Act 1975 (c.71), Schedule 15, paragraph 6.
1972 c.68. Paragraph 1A of Schedule 2 was inserted by section 28 of the Legislative and Regulatory Reform Act 2006 (c. 51).
Articles 3 and 16(1) and (2) of the Legislative Reform (Health and Safety Executive) Order 2008 (S.I. 2008/960) substituted a new version of section 50(1) for the previous version and inserted section 50(1AA). The extent of the requirement to consult pursuant to section 50(1) was narrowed by the insertion of section 50(1A) into the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 by the Railways Act 2005 (“the 2005 Act”) (c.14), Schedule 3, paragraph 13.
The meaning of “railway safety purposes” under Schedule 3 of the 2005 Act which is relevant to the obligation to consult has been amended by the Railways Act 2005 (Amendment) Regulations 2006 (S.I. 2006/556).
ISBN 9789211391343 (2009 edition).
ISBN 9789211391336 (2009 edition).
See section 1(1) of the Ministry of Defence Police Act 1987 (c.4).
Cm 3812; COTIF was modified by the Protocol signed at Vilnius on 3rd June 1999 (Cm 4873).
OJ No L260, 30.9.2008, p.13.
2004 c.21; section 1(2)(d) was amended by the Civil Contingencies Act 2004 (c.36), Schedule 2, Part 1, paragraph 10(1) and (2).
ISBN 9788086206394 (2009 edition).
OJ No L138, 1.6.1999, p.20; last amended by Commission Directive 2002/50/EC of 6th June 2002 (OJ No L149, 7.6.2002, p.28).
1994 c.22; paragraph 2 of Schedule 3 to the Finance Act 1997 replaced the existing section 21(1) with a new version.
ISBN 9780113413263 (2009 edition).
S.I. 1987/37; to which there are amendments not relevant to these Regulations.
S.I. 2004/568; revoked by S.I. 2007/1573.
S.I. 1983/1140, amended by S.I. 1999/303, 2004/568 and 2007/1573.
1984 c.27; section 121A was inserted by the New Roads and Street Works Act 1991 (c.22), Schedule 8, Part 2, paragraph 70 and amended by the Greater London Authority Act 1999 (c.29), section 271 and S.I. 1999/1820 and 2001/1400.
S.I. 2006/557; amended by S.I. 2007/1573; there is another amendment not relevant to these Regulations.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Instrument
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As Enacted or Made): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was enacted or made. No changes have been applied to the text.
Explanatory Memorandum
Explanatory Memorandum sets out a brief statement of the purpose of a Statutory Instrument and provides information about its policy objective and policy implications. They aim to make the Statutory Instrument accessible to readers who are not legally qualified and accompany any Statutory Instrument or Draft Statutory Instrument laid before Parliament from June 2004 onwards.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as enacted version that was used for the print copy
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
Impact Assessments
Impact Assessments generally accompany all UK Government interventions of a regulatory nature that affect the private sector, civil society organisations and public services. They apply regardless of whether the regulation originates from a domestic or international source and can accompany primary (Acts etc) and secondary legislation (SIs). An Impact Assessment allows those with an interest in the policy area to understand:
- Why the government is proposing to intervene;
- The main options the government is considering, and which one is preferred;
- How and to what extent new policies may impact on them; and,
- The estimated costs and benefits of proposed measures.
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as made version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources