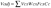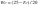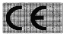- Latest available (Revised)
- Original (As made)
The Ecodesign for Energy-Using Products Regulations 2007
You are here:
- UK Statutory Instruments
- 2007 No. 2037
- Schedules only
More Resources
Status:
This is the original version (as it was originally made).
Regulation 2
SCHEDULE 1Listed products
PART 1Listed products and implementing measures
1. “Listed product” means—
(a)a boiler or an appliance;
(b)a refrigerator appliance;
(c)a ballast for fluorescent lighting,
as defined in this Schedule.
2. “Implementing measure” in relation to—
(a)a boiler or an appliance, means Council Directive 92/42/EEC on efficiency requirements for new hot water boilers fired with liquid or gaseous fuels(1);
(b)a refrigerator appliance, means Directive 96/57/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on energy efficiency requirements for household electric refrigerators, freezers and combinations thereof(2);
(c)a ballast for fluorescent lighting, means Directive 2000/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on energy efficiency requirements for ballasts for fluorescent lighting(3).
PART 2Boilers and appliances
1. The following definitions have effect—
(a)“a boiler” means the combined boiler body-burner unit which—
(i)is designed to transmit to water the heat released from burning;
(ii)is fired by liquid or gaseous fuels; and
(iii)has a rated output of no less than 4kW and no more than 400kW;
and
(b)“an appliance” means—
(i)the boiler body designed to have a burner fitted; or
(ii)the burner designed to be fitted to a boiler body.
2. The following are not within the definition in paragraph 1—
(a)a boiler capable of being fired by fuels other than liquid or gaseous fuels, including solid fuels;
(b)equipment for the instantaneous preparation of hot water;
(c)a boiler designed to be fired by fuels the properties of which differ appreciably from liquid or gaseous fuels commonly marketed;
(d)a cooker or an appliance designed mainly to heat the premises in which they are installed and, as a subsidiary function, to supply hot water for central heating and sanitary hot water;
(e)an appliance with a rated output of less than 6kW using gravity circulation and designed solely for the production of stored sanitary hot water;
(f)a boiler manufactured on a one-off basis; or
(g)cogeneration units as defined in Directive 2004/8/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on the promotion of cogeneration based on a useful heat demand in the internal energy market(4).
PART 3Refrigerator appliances
1. “A refrigerator appliance” means—
(a)a refrigerator;
(b)a frozen food storage cabinet;
(c)a food freezer; or
(d)a combination of any of (a), (b) or (c),
for household use supplied by mains electricity.
2. The following are not within the definition in paragraph 1—
(a)a refrigerator appliance manufactured on a one-off basis;
(b)a refrigerator appliance capable of using energy sources apart from mains electricity, in particular accumulators; or
(c)a refrigerator appliance working on the absorption principle.
PART 4Ballasts for fluorescent lighting
1. “A ballast for fluorescent lighting” means a ballast—
(a)operated by mains electricity; and
(b)used for fluorescent lighting,
as defined in point 3.4 of European Standard EN 50294.
2. The following are not within the definition in paragraph 1—
(a)a ballast integrated within a lamp;
(b)a ballast—
(i)designed specifically for a luminaire to be mounted in furniture;
(ii)which forms a non-replaceable part of the luminaire; and
(iii)which cannot be tested separately from the luminaire, according to point 2.1.3 of European Standard 60920;
or
(c)a ballast to be exported from the Community either as a single component or incorporated in a luminaire.
Regulation 3
SCHEDULE 2Product requirements
PART 1Introduction
1. This Schedule sets out in relation to a listed product the requirements that must be met by that product.
PART 2Boilers and appliances
1. A boiler or an appliance must comply with the useful efficiency requirements—
(a)at rated output (that is operating at rated output Pn expressed in kW, at an average boiler-water temperature of 70 degrees C); and
(b)at part load (that is operating at 30 per cent part load, at an average boiler-water temperature which varies according to the type of boiler),
set out in the table in paragraph 2.
2. The table referred to in paragraph 1—
Useful efficiency requirements
| Type of Boiler | Range of power output | Efficiency at rated output | Efficiency at part load | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
(1) Including a condensing boiler using liquid fuels | |||||
(2) Temperature of boiler water supply | |||||
| kW | Average boiler-water temperature expressed in degrees C | Efficiency requirement expressed in percent | Average boiler-water temperature expressed in degrees C | Efficiency requirement expressed in per cent | |
| Standard | 4 to 400 | 70 | Greater than or equal to 84+2 log Pn | Greater than or equal to 50 | Greater than or equal to 80 + 3 log Pn |
| Low temperature(1) | 4 to 400 | 70 | Greater than or equal to 87.5+1.5 log Pn | 40 | Greater than or equal to 87.5 + 1.5 log Pn |
| Gas condensing | 4 to 400 | 70 | Greater than or equal to 91 + 1 log Pn | 30(2) | Greater than or equal to 97 + 1 log Pn |
3. A boiler or an appliance with a dual function of—
(a)heating premises; and
(b)providing sanitary hot water,
must comply with paragraph 1 to the extent of the heating function only.
4. A boiler which is—
(a)a back-boiler; or
(b)a boiler designed to be installed in the living space,
must be treated as a standard boiler but its efficiency at rated output and part load may be 4 per cent less than shown in the table in paragraph 2.
PART 3Refrigerator appliances
1. If a refrigerator appliance is within categories 1 to 9 as described in table 1 in paragraph 2, the maximum allowable electricity consumption (Emax) of that appliance, expressed in kWh per 24 hours, is set out in column 3 of that table.
2. The table referred to in paragraph 1—
Table 1
Requirements for maximum allowable electricity consumption – appliances in categories 1 to 9
| Category | Description | Emax (kWh/.24h) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Refrigerator without low temperature compartment (being any compartment with a temperature at or below -6 degrees C) | (0.207 x Vadj + 218) / 365 |
| 2 | Refrigerator/chiller with compartment at 5 degrees C and/or 12 degrees C | (0.207 x Vadj + 218) / 365 |
| 3 | Refrigerator with no-star low temperature compartment | (0.207 x Vadj + 218) / 365 |
| 4 | Refrigerator with low temperature compartment (*) | (0.557 x Vadj + 166) / 365 |
| 5 | Refrigerator with low temperature compartment (**) | (0.402 x Vadj + 206) / 365 |
| 6 | Refrigerator with low temperature compartment (***) | (0.573 x Vadj + 206) / 365 |
| 7 | Refrigerator/freezer, with freezer compartment (****) | (0.697 x Vadj + 272) / 365 |
| 8 | Food freezer, upright | (0.434 x Vadj + 262) / 365 |
| 9 | Food freezer, chest | (0.480 x Vadj + 195) / 365 |
3. If a refrigerator appliance—
(a)has more than 2 doors; or
(b)is not described in table 1,
the maximum allowable electricity consumption (Emax) of that appliance as described in columns 1 and 2 of table 2 in paragraph 4, expressed in kWh per 24 hours, is set out in column 3 of that table.
4. Table 2 referred to in paragraph 3—
Table 2
Requirements for maximum allowable electricity consumption – other appliances
| Temperature of the coldest compartment | Category | Emax (kWh/24 hours) |
|---|---|---|
| > - 6 degrees C | 1/2/3 | (0.207 x Vadj + 218) / 365 |
| - 6 degrees C(*) | 4 | (0.557 x Vadj + 166) / 365 |
| - 12 degrees C(**) | 5 | (0.402 x Vadj + 219) / 365 |
| - 18 degrees C (***) | 6 | (0.573 x Vadj + 206) / 365 |
| - 18 degrees C(****) | 7 | (0.697 x Vadj + 272) / 365 |
5. The categories 1 to 7 referred to in column 2 of table 2 are the same categories of refrigerator appliance numbered 1 to 7 referred to in column 1 of table 1.
6. The following have effect in respect of tables 1 and 2—
7. For the purposes of paragraph 6—
Vadj is the value of the adjusted volume (in litres);
Vc is the net volume (in litres) of a given type of compartment in the appliance;
Tc is the design temperature in each compartment (in degrees C);
Fc is a factor which equals—
1.2 for no-frost compartments; or
1 for other compartments;
Cc is—
1 for refrigeration appliances belonging to the normal (N) and subnormal (SN) climate classes;
Xc for refrigeration appliances belonging to the sub-tropical (ST) climate class; or
Yc for refrigeration appliances belonging to the tropical (T) climate class;
Xc and Yc are weighting co-efficients defined in paragraph 8.
8. The following table defines the co-efficients Xc and Yc referred to in paragraph 7—
Table 3
Table of weighting co-efficients Xc and Yc, according to the temperature of the compartment
| Xc | Yc | |
|---|---|---|
| Cellar compartment | 1.25 | 1.35 |
| Fresh food compartment | 1.20 | 1.30 |
| 0 degrees C compartment | 1.15 | 1.25 |
| 1-star (*) compartment | 1.12 | 1.20 |
| 2-star (**) compartment | 1.08 | 1.15 |
| 3 (***) and 4 (****) star compartments | 1.05 | 1.10 |
9. For the purposes of this Part, a manufacturer must establish the electricity consumption of a refrigerator appliance in accordance with European Standard EN 153.
PART 4Ballasts for fluorescent lighting
1. A ballast for fluorescent lighting must be allocated to a category as described in table 1 in paragraph 3.
2. In respect of—
(a)the category of ballast shown in column 1 of table 2 in paragraph 4; and
(b)the lamp power shown for that category in column 2 of table 2,
the maximum input value of a ballast lamp circuit shall be the value shown in column 3 of table 2.
3. Table 1 referred to in paragraph 1—
Table 1
Categories of ballast
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| 1 | Ballast for linear lamp type |
| 2 | Ballast for compact 2 tubes lamp type |
| 3 | Ballast for compact 4 tubes flat lamp type |
| 4 | Ballast for compact 4 tubes lamp type |
| 5 | Ballast for compact 6 tubes lamp type |
| 6 | Ballast for compact 2 D lamp type |
4. Table 2 referred to in paragraph 2—
Table 2
Maximum input power of a ballast-lamp circuit
| Ballast category | Lamp Power | Maximum input power of Ballast-lamp circuits | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Column 1 | Column 2 | Column 3 | |||
| 50 Hz | HF | ||||
| 1 | 15W | 13.5W | 23W | ||
| 18W | 16W | 26W | |||
| 30W | 24W | 38W | |||
| 36W | 32W | 43W | |||
| 38W | 32W | 45W | |||
| 58W | 50W | 67W | |||
| 70W | 60W | 80W | |||
| 2 | 18W | 16W | 26W | ||
| 24W | 22W | 32W | |||
| 36W | 32W | 43W | |||
| 3 | 18W | 16W | 26W | ||
| 24W | 22W | 32W | |||
| 36W | 32W | 43W | |||
| 4 | 10W | 9.5W | 16W | ||
| 13W | 12.5W | 19W | |||
| 18W | 16.5W | 26W | |||
| 26W | 24W | 34W | |||
| 5 | 18W | 16W | 26W | ||
| 26W | 24W | 34W | |||
| 6 | 10W | 9W | 16W | ||
| 16W | 14W | 23W | |||
| 21W | 19W | 29W | |||
| 28W | 25W | 36W | |||
| 38W | 34W | 45W | |||
5. For a ballast for fluorescent lighting designed for a lamp which falls between two values shown in table 2, the maximum input value of a ballast lamp circuit must be calculated by linear interpolation between the two values of maximum power for the two lamps which are closest in table 2 to the lamp in question.
6. For the purposes of this Part, a manufacturer must establish the electricity consumption for a ballast for fluorescent lighting in accordance with European Standard EN 50294.
Regulation 4
SCHEDULE 3Conformity assessment procedures applicable to a listed product
PART 1Introduction
1. This Schedule sets out the conformity assessment procedure or procedures applicable to a listed product.
2. “The testing and checking process” has the meaning given in chapter 3 of Part 1 to Schedule 4.
3. References to a manufacturer include—
(a)an authorised representative; or
(b)an importer of a listed product,
where such person undertakes some or all of a conformity assessment procedure.
PART 2Boilers and appliances
1. The conformity assessment procedures applicable to a boiler or an appliance are—
(a)module B with the additional provisions in paragraphs 2 and 3; and
(b)the following as chosen by the manufacturer—
(i)module C and the testing and checking process;
(ii)module D; or
(iii)module E.
2. The following additional technical documentation must form part of the general technical documentation to be included with the application made under paragraph 2 of module B—
(a)a general type-description;
(b)conceptual design and manufacturing drawings and diagrams of components, sub-assemblies and circuits;
(c)descriptions and explanations necessary for the understanding of the drawings and diagrams and the operation of the product;
(d)results of design calculations made and examinations carried out; and
(e)test reports.
3. A representative sample of the boiler or appliance, and such further examples as the notified body may request, must be made available to the notified body for examination and testing.
PART 3Refrigerator appliances
1. The conformity assessment procedures applicable to a refrigerator appliance are—
(a)module A with the additional provisions in paragraph 2; and
(b)the electricity consumption procedure described in paragraph 3.
2. The following additional technical documentation must form part of the general technical documentation to be established under paragraph 1 of module A—
(a)information, including drawings as relevant, on the main design features of the model, in particular on items which appreciably affect its electricity consumption, including dimensions, volume(s), compressor characteristics and special features;
(b)any operating instructions;
(c)the results of electricity consumption procedure carried out under paragraph 3; and
(d)details of the conformity of those results compared with the energy consumption provisions of the product requirements.
3. The electricity consumption procedure referred to in paragraph 1 means—
(a)if the electricity consumption of a refrigeration appliance is less than or equal to the maximum allowable electricity consumption plus 15%, the manufacturer may make a declaration of conformity; or
(b)if the electricity consumption of a refrigeration appliance is greater than the maximum allowable electricity consumption plus 15%, the manufacturer must test a further three appliances and if the arithmetic mean of the electricity consumptions of those three appliances is—
(i)less than or equal to the maximum allowable electricity consumption plus 10%, the manufacturer may make a declaration of conformity; or
(ii)in excess of the maximum allowable electricity consumption plus 10%, the manufacturer must not make a declaration of conformity.
4. For the purposes of paragraph 3, a manufacturer must establish the electricity consumption of a refrigerator appliance in accordance with European Standard EN 153.
PART 4Ballasts for fluorescent lighting
1. The conformity assessment procedure applicable to a ballast for fluorescent lighting is module A with the additional provisions in paragraph 2.
2. The following additional technical documentation must form part of the general technical documentation to be established under paragraph 1 of module A—
(a)information, including drawings as relevant, on the main design features of the model, in particular on items which appreciably affect its electricity consumption;
(b)any operating instructions;
(c)the results of electricity consumption measurements carried out in accordance with European Standard EN 50294; and
(d)details of the conformity of the measurements carried out under paragraph (c) compared with the energy consumption provisions of the product requirements.
Regulation 4
SCHEDULE 4Modules for conformity assessment
PART 1General
CHAPTER 1Miscellaneous
1. A notified body referred to in this Schedule means a notified body appointed by agreement between that body and one or more of the following—
(a)the manufacturer of a listed product;
(b)an authorised representative;
(c)an importer of a listed product.
2. In the remaining provisions of this Schedule, references to a manufacturer include—
(a)an authorised representative; or
(b)an importer of a listed product,
where such person undertakes some or all of a conformity assessment procedure.
3. “Equivalent standards” means standards equivalent to the harmonised standards, including national standards notified by the Commission pursuant to Article 5 of Annex II.B to the Council Resolution of 7 May 1985(5).
4. A notified body must carry out tests or examinations—
(a)at such place as the manufacturer and notified body agree; and
(b)so far as appropriate, in accordance with—
(i)the harmonised standards; or
(ii)equivalent standards.
5. A notified body must, under module B—
(a)determine the elements of the listed product, or the design for such a product, which have been made or designed in accordance with a harmonised standard or equivalent standard; and
(b)in respect of elements not made or designed in accordance with a harmonised standard or equivalent standard, determine how those elements conform to the product requirements.
6. A notified body must ensure that—
(a)in module D, at least one member of the team which carries out the determination of the application has experience of the product technology in question;
(b)in module E, at least one member of the team which carries out the determination of the application has experience as an assessor in the product technology in question; and
(c)in modules D and E, it makes at least one inspection visit to the premises of the manufacturer.
7. Expressions used in this Schedule which are used in Council Decision 93/465/EEC concerning the modules for the various phases of the conformity assessment procedures and the rules for the affixing and use of the CE conformity marking, which are intended to be used in the technical harmonisation directives(6), have the same meaning as they do in that Decision.
CHAPTER 2General technical documentation
8. The general technical documentation means the documentation necessary to enable an assessment of the conformity of a listed product to the product requirements, including as appropriate documentation concerning—
(a)the design, manufacture and operation of the product;
(b)the harmonised standards or equivalent standards applied, or to be applied, to the product.
9. The provision of the documentation under paragraph 8 may be satisfied by the supply of equivalent documentation required under Community legislation other than the implementing measure relating to a listed product.
CHAPTER 3Testing and checking process
10. The testing and checking process means the notified body carries out product checks—
(a)at random intervals; and
(b)on an adequate sample taken on site by the notified body.
11. If the testing and checking process demonstrates that a listed product conforms to the product requirements, the notified body must permit the manufacturer to affix the identification number or symbol of the notified body to the listed product during the manufacturing process.
CHAPTER 4Notified bodies and non-conformity
12. Where a notified body determines that a listed product does not conform, or will not conform, to the product requirements, it must, subject to paragraph 13, request the manufacturer to provide such further information or to take such additional steps that it believes are necessary to demonstrate conformity.
13. If—
(a)no such further information or steps are possible; or
(b)such information or steps do not demonstrate conformity,
the notified body must give the manufacturer a non-conformity notice.
14. “A non-conformity notice” means a written notice that—
(a)states that the notified body is not satisfied that a listed product conforms, or will conform, to the product requirements; and
(b)gives details of the non-conformity.
15. Where a notified body has given a non-conformity notice and prior to that notice has given to the manufacturer —
(a)an EC type-examination certificate or an EC design examination certificate; or
(b)an approval to a quality assurance procedure under modules D or E,
the notified body must state in the non-conformity notice if, and the extent to which, the giving of the notice withdraws a certificate or approval, including any additions or modifications to a certificate or approval.
PART 2Module A (internal production control)
1. The manufacturer must establish the general technical documentation.
2. The general technical documentation must be kept with the declaration of conformity.
3. The manufacturer must take all necessary measures to ensure that the manufacturing process of a listed product ensures that the product complies with the general technical documentation.
PART 3Module B (EC type-examination)
1. The manufacturer must make a written application to a notified body for that body to provide an EC type-examination certificate.
2. The application must include—
(a)the name and address of the manufacturer and, if appropriate, the authorised representative of the manufacturer;
(b)a declaration that an application has not been made to another notified body; and
(c)the general technical documentation.
3. The notified body must—
(a)examine the general technical documentation;
(b)determine if the type has been manufactured in accordance with that documentation;
(c)carry out tests and examinations to determine whether—
(i)elements designed in accordance with—
(aa)the harmonised standards; or
(bb)equivalent standards,
meet those standards;
and
(ii)elements not so designed conform to the product requirements.
4. If a notified body is satisfied that the type conforms to the product requirements, it must—
(a)give to the manufacturer an EC type-examination certificate;
(b)annex to that certificate a list of the general technical documentation; and
(c)keep a copy of the certificate and the annexed list of general technical documentation.
5. An EC type-examination certificate must be in writing and include—
(a)the name and address of the manufacturer;
(b)the conclusions of the tests and examinations referred to in paragraph 3;
(c)any conditions of validity of the certificate; and
(d)the data necessary to identify the approved type.
6. If a manufacturer makes modifications to a listed product that affect its conformity to the product requirements, the manufacturer must make an application to the notified body that granted the EC type-examination certificate for an additional approval to that certificate.
7. Where an application is made for an additional approval to a EC type-examination certificate—
(a)the manufacturer must make that application, so far as appropriate, in accordance with paragraph 2; and
(b)the notified body must—
(i)comply with paragraph 3; and
(ii)if it is satisfied that the type continues to conform to the product requirements, comply with paragraph 4 as if reference to an EC type-examination certificate were a reference to an additional approval to that certificate.
8. Relevant documentation under regulation 10 includes—
(a)the EC type-examination certificate; and
(b)any additional approval.
PART 4Module C (conformity to type)
1. The manufacturer must take all necessary measures to ensure that the manufacturing process of a listed product ensures that the product—
(a)complies with the type as described in the EC type-examination certificate; and
(b)conforms to the product requirements.
PART 5Module D (production quality assurance)
1. The manufacturer must operate an approved quality system in respect of—
(a)the production of the product; and
(b)the final product inspection and testing.
2. A quality system is approved if it is approved by a notified body and it meets the following criteria—
(a)it must ensure compliance of a listed product with the type as described in the EC type-examination certificate and that it conforms to the product requirements;
(b)the elements, requirements and provisions adopted by the manufacturer must be documented in a systematic and orderly manner in the form of written policies, procedures and instructions; and
(c)the quality system documentation must—
(i)permit a consistent interpretation of the quality programmes, plan, manual and records; and
(ii)include the matters contained in paragraph 3.
3. The matters referred to in paragraph 2(c)(ii) are that the quality system documentation contain an adequate description of—
(a)the quality objectives and the organisational structure, responsibilities and powers of the management with regard to product quality;
(b)the manufacturing, quality control and quality assurance techniques, processes and systematic actions that will be used;
(c)the examinations and tests that will be carried out before, during and after manufacture and the frequency with which they will be carried out;
(d)the quality records, including inspection reports and test data, calibration data and qualification reports of the personnel concerned; and
(e)the means to monitor the achievement of the required product quality and the effective operation of the quality system.
4. A manufacturer must apply for approval of his quality system to a notified body and must include in that application—
(a)all relevant information for the product category envisaged;
(b)the documentation concerning the quality system; and
(c)if applicable—
(i)the general technical documentation of the approved type; and
(ii)a copy of the EC type-examination certificate.
5. Where a notified body receives an application in accordance with paragraph 4, the it must—
(a)determine the application; and
(b)if it is satisfied that the quality system meets the criteria contained or referred to in paragraph 2, the notified body must provide its approval to the manufacturer.
6. An approval under paragraph 5 must be in writing and include—
(a)the reasons for the decision; and
(b)the conclusions of the examinations and tests.
7. If a manufacturer intends to modify the approved quality system—
(a)he must inform in writing the notified body that approved the quality system; and
(b)the notified body must determine whether or not the proposed modification requires a re-assessment of the quality system.
8. If the notified body determines that a re-assessment is required, the procedures in paragraphs 4 to 6 apply in respect of an application for assessment of the quality system as proposed to be modified.
9. A notified body must carry out—
(a)periodic audits of the quality system of the manufacturer; and
(b)periodic unannounced visits to the premises of the manufacturer,
whose quality system it has approved in order to determine that the manufacturer is maintaining and applying the quality system.
10. A notified body must inform the manufacturer of the results of the audit and visit by providing written audit and visit reports.
11. In relation to paragraph 9, a manufacturer must—
(a)allow the notified body access to the locations of manufacture, inspection and testing, and storage;
(b)provide all necessary documentation to the notified body, including—
(i)the documentation concerning the quality system; and
(ii)the quality records, including inspection reports and test data, calibration data and qualification reports of the personnel concerned;
and
(c)in respect of visits by the notified body, carry out or allow the notified body to carry out tests necessary to determine that the quality system is functioning correctly.
12. Relevant documentation under regulation 10 includes—
(a)the documentation concerning the quality system submitted with an application for approval;
(b)approvals in relation to the quality system;
(c)details of the modifications to the quality system; and
(d)audit and visit reports.
PART 6Module E (product quality assurance)
1. The manufacturer must operate an approved quality system in respect of the final product inspection and testing.
2. Paragraphs 2 to 12 of module D (production quality assurance) apply save that the following are omitted—
(a)paragraph 3(b); and
(b)in paragraph 11(a), the word “manufacture”.
Regulation 4
SCHEDULE 5Declaration of conformity
1. A person who makes a declaration of conformity declares that a listed product to which the declaration relates, conforms to the product requirements for that product.
2. A declaration of conformity—
(a)must be in writing; and
(b)may be in respect of more than one listed product.
3. A declaration of conformity must include—
(a)the name and address of the person making it;
(b)a description of the model sufficient for unambiguous identification;
(c)where appropriate—
(i)the references of the harmonised standards applied;
(ii)the other technical standards and specifications used; and
(iii)the reference to other Community legislation, not referred to in paragraph 4, providing for the affixing of the CE mark that is applied;
and
(d)the identification and signature of the individual empowered to bind the person making the declaration.
4. A declaration of conformity must include the title of the implementing measure applicable to a listed product as shown in the following table—
Table of listed products and implementing measures
| listed product | Title of implementing measure |
|---|---|
| 1. A boiler or an appliance | Council Directive 92/42/EEC on efficiency requirements for new hot water boilers fired with liquid or gaseous fuels |
| 2. A refrigerator appliance | Directive 96/57/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on energy efficiency requirements for household electric refrigerators, freezers and combinations thereof |
| 3. A ballast for fluorescent lighting | Directive 2000/55/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council on energy efficiency requirements for ballasts for fluorescent lighting |
Regulation 4
SCHEDULE 6CE conformity marking
PART 1General requirements
1. A CE conformity marking must be in the following form—
2. A CE conformity marking must have a height of at least 5mm.
3. Subject to paragraph 2, if a CE conformity marking is reduced or enlarged, the marking must maintain the proportions shown in paragraph 1.
PART 2Additional requirements
1. Where a CE conformity marking is affixed in relation to a boiler or an appliance, the marking must further include the last two figures of the year in which the mark was affixed.
2. Where a ballast for fluorescent lighting is placed on the market incorporated within a luminaire, the CE conformity marking must also be affixed to the luminaire and its packaging.
Regulation 11
SCHEDULE 7Criteria to be met by notified bodies
1. A notified body must act—
(a)with the highest degree of professional integrity and technical competence;
(b)free from all pressures and inducements which might influence the decision of the notified body, in particular pressures and inducements—
(i)which are financial; or
(ii)from a person with an interest in the decision;
and
(c)with regard to any commercial confidentiality that may be attached to the information supplied to it.
2. A notified body must possess the necessary—
(a)staff and facilities; and
(b)equipment, including specialist equipment,
to enable it to perform the obligations and exercise the powers of a notified body in relation to the listed products for which it is approved under regulation 11.
3. The staff of a notified body must be impartial and those who perform tests must have—
(a)sound technical and professional training;
(b)satisfactory knowledge and experience of the requirements of the tests;
(c)the ability to draw up the certificates, records and reports required to authenticate the performance of the tests; and
(d)remuneration that is not dependent on the number or result of the tests.
4. A notified body must ensure that any other person it engages to assist it to perform any of its obligations or exercise any of its powers meets the criteria in this Schedule.
Regulations 15 and 21
SCHEDULE 8Appeals
1. An appeal must be made within two months of the date of, as appropriate, the non-conformity notice or the enforcement notice.
2. In respect of—
(a)a non-conformity notice, the parties to the appeal may agree a late appeal;
(b)an enforcement notice, the appeal body may allow a late appeal.
3. Where an appeal is brought, this does not suspend the operation of the notice.
4. On the determination of an appeal, the appeal body may—
(a)affirm the notice;
(b)withdraw it;
(c)make a further notice, whether or not it affirms or withdraws the original notice,
and may do so subject to such conditions as the appeal body sees fit.
5. An appeal body may deal with an appeal in such manner as it sees fit.
Regulation 20
SCHEDULE 9Powers of enforcing authorities
PART 1Powers of entry
1. An authorised person—
(a)may enter any premises for the purposes of ensuring that the provisions referred to in regulation 18(1) are being complied with; and
(b)must produce, if so required, a document showing his authority.
2. The power may be exercised—
(a)at all reasonable hours; or
(b)in an emergency, at any time and if need be by reasonable force.
3. An authorised person may take with him—
(a)such other persons as he considers necessary, including a constable;
(b)any equipment or materials required for any purpose for which the power of entry is being exercised;
(c)any representative of the European Commission acting for the purpose of the enforcement of a Community obligation.
4. A person entering unoccupied premises must leave them as effectively secured against unauthorised entry as he found them.
5. Admission to any premises used only as a private dwelling-house must not be demanded as of right unless—
(a)24 hours notice of the intended entry has been given to the occupier; or
(b)the entry is in accordance with a warrant.
6. The reference to “premises” in relation to powers of entry includes any—
(a)place;
(b)caravan, vehicle or trailer;
(c)container;
(d)stall or moveable structure;
(e)ship or aircraft.
PART 2Warrants
1. If a justice of the peace, on sworn information in writing, is satisfied—
(a)that there are reasonable grounds to enter any premises; and
(b)that any of the conditions in paragraph 2 are met,
he may by warrant signed by him authorise an authorised person and any other person to enter the premises, if need be by reasonable force.
2. The conditions referred to in paragraph 1—
(a)admission to the premises has been refused, or a refusal is expected, and in either case that notice to apply for a warrant has been given to the occupier;
(b)asking for admission, or the giving of such a notice, would defeat the object of the entry;
(c)entry is required urgently;
(d)the premises are unoccupied or the occupier is temporarily absent.
3. A warrant continues in force for one month.
4. Reference to a justice of the peace—
(a)in Scotland includes a sheriff;
(b)in Northern Ireland is a reference to a lay magistrate.
PART 3Powers on entry
1. An authorised person who has entered any premises in accordance with this Schedule may, on or in the vicinity of the premises,—
(a)carry out any examination or investigation;
(b)take measurements, photographs or recordings;
(c)take samples;
(d)dismantle any thing;
(e)subject any thing to any process or test;
(f)take possession of and detain any thing for so long as may be necessary—
(i)in relation to the exercise of any other powers under this Schedule;
(ii)to ensure that it is not tampered with before its examination is complete; or
(iii)to ensure that it is available for use in any proceedings;
(g)require the production of records or extracts of records and inspect and take copies of such records or extracts;
(h)require any person to afford him facilities and assistance in relation to matters within the control or responsibility of that person.
2. An authorised person must avoid destruction or damage to the premises or things within it unless that is necessary in the reasonable exercise of his powers.
3. If a person claims to be entitled to compensation in respect of the exercise of the powers under paragraph 1, such a claim—
(a)in England and Wales, must be referred to the arbitration of a single arbitrator appointed by agreement between the enforcing authority in question and the person who makes the claim or, in default of agreement, appointed by the Secretary of State;
(b)in Scotland, must be referred to the arbitration of an arbiter, appointed by agreement between the enforcing authority in question and the person who makes the claim or, in default of agreement, appointed by the Scottish Ministers; or
(c)in Northern Ireland, must be referred to and determined by the Lands Tribunal for Northern Ireland.
PART 4Test purchases and testing
1. An authorised person may purchase any article or substance to determine whether or not the provisions referred to in regulation 18(1) have been complied with and may carry out such tests and examinations on the article or substance in order to do so.
2. An enforcing authority must comply with paragraph 3 if—
(a)it has acquired any article or substance under the provisions of this Schedule; and
(b)it commences, or causes to be commenced, any proceedings under these Regulations by reason of tests and examinations on such article or substance.
3. Where paragraph 2 applies, an enforcing authority must if requested to do so, and if it is practicable in the circumstances, allow—
(a)a person who is a party to the proceedings; and
(b)any other person with an interest in the article or substance,
to have that article or substance tested.
4. An article or substance includes a listed product or any part of it.
PART 5Notices
1. The enforcing authority may, by notice served on any person, require that person to furnish such information as is specified in the notice, in such form and within such period following service of the notice or at such time as is so specified.
2. If the enforcing authority is of the opinion that a person has contravened, is contravening or is likely to contravene the provisions referred to in regulation 18(1), the enforcing authority may serve on him a notice (an “enforcement notice”).
3. An enforcement notice must—
(a)state that the enforcing authority is of that opinion;
(b)specify the matters constituting the contravention or the matters making it likely that the contravention will arise, as the case may be;
(c)specify the steps that must be taken to remedy the contravention or to remedy the matters making it likely that the contravention will arise, as the case may be; and
(d)specify the period within which those steps must be taken.
4. An enforcement notice may require that a listed product, or elements of it, is withdrawn from the market or from service.
5. The enforcing authority may withdraw an enforcement notice at any time.
6. If a person fails to comply with an enforcement notice, the enforcing authority may do what that person was required to do and may recover from him any expenses reasonably incurred in doing so.
Regulation 28
SCHEDULE 10Revocations
| Statutory Instrument Number | Citation | Extent of revocation |
|---|---|---|
| S.I. 1993/3083 | The Boiler (Efficiency) Regulations 1993 | All |
| S.I. 1994/3083 | The Boiler (Efficiency) (Amendment) Regulations 1994 | All |
| S.I. 1997/1941 | The Energy Efficiency (Refrigerators and Freezers) Regulations 1997 | All |
| S.I. 2001/3142 | The Energy Information and Energy Efficiency (Miscellaneous Amendments) Regulations 2001 | Regulation 11 |
| S.I. 2001/3316 | The Energy Efficiency (Ballasts for Fluorescent Lighting) Regulations 2001 | All |
| S.I. 2006/170 | The Boiler (Efficiency) (Amendment) Regulations 2006 | All |
O.J. No. L167, 22.6.1992, p. 17 as last amended by Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (O.J. No. L191, 22.7.2005, p. 29).
O.J. No. L236, 18.9.1996, p. 36 as last amended by Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (O.J. No. L191, 22.7.2005, p. 29).
O.J. No. L279, 1.11.2000, p. 33 as last amended by Directive 2005/32/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council (O.J. No. L191, 22.7.2005, p. 29).
O.J. No. L52, 21.2.2004, p. 50.
O.J. No. C136, 4.6.1985, p. 1.
O.J. No. L220, 30.8.1993, p. 23.
Options/Help
Print Options
PrintThe Whole Instrument
PrintThe Schedules only
Legislation is available in different versions:
Latest Available (revised):The latest available updated version of the legislation incorporating changes made by subsequent legislation and applied by our editorial team. Changes we have not yet applied to the text, can be found in the ‘Changes to Legislation’ area.
Original (As Enacted or Made): The original version of the legislation as it stood when it was enacted or made. No changes have been applied to the text.
Explanatory Memorandum
Explanatory Memorandum sets out a brief statement of the purpose of a Statutory Instrument and provides information about its policy objective and policy implications. They aim to make the Statutory Instrument accessible to readers who are not legally qualified and accompany any Statutory Instrument or Draft Statutory Instrument laid before Parliament from June 2004 onwards.
More Resources
Access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item from this tab. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as enacted version that was used for the print copy
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- correction slips
- links to related legislation and further information resources
More Resources
Use this menu to access essential accompanying documents and information for this legislation item. Dependent on the legislation item being viewed this may include:
- the original print PDF of the as made version that was used for the print copy
- correction slips
Click 'View More' or select 'More Resources' tab for additional information including:
- lists of changes made by and/or affecting this legislation item
- confers power and blanket amendment details
- all formats of all associated documents
- links to related legislation and further information resources